8.0 Final Hardware Implementation
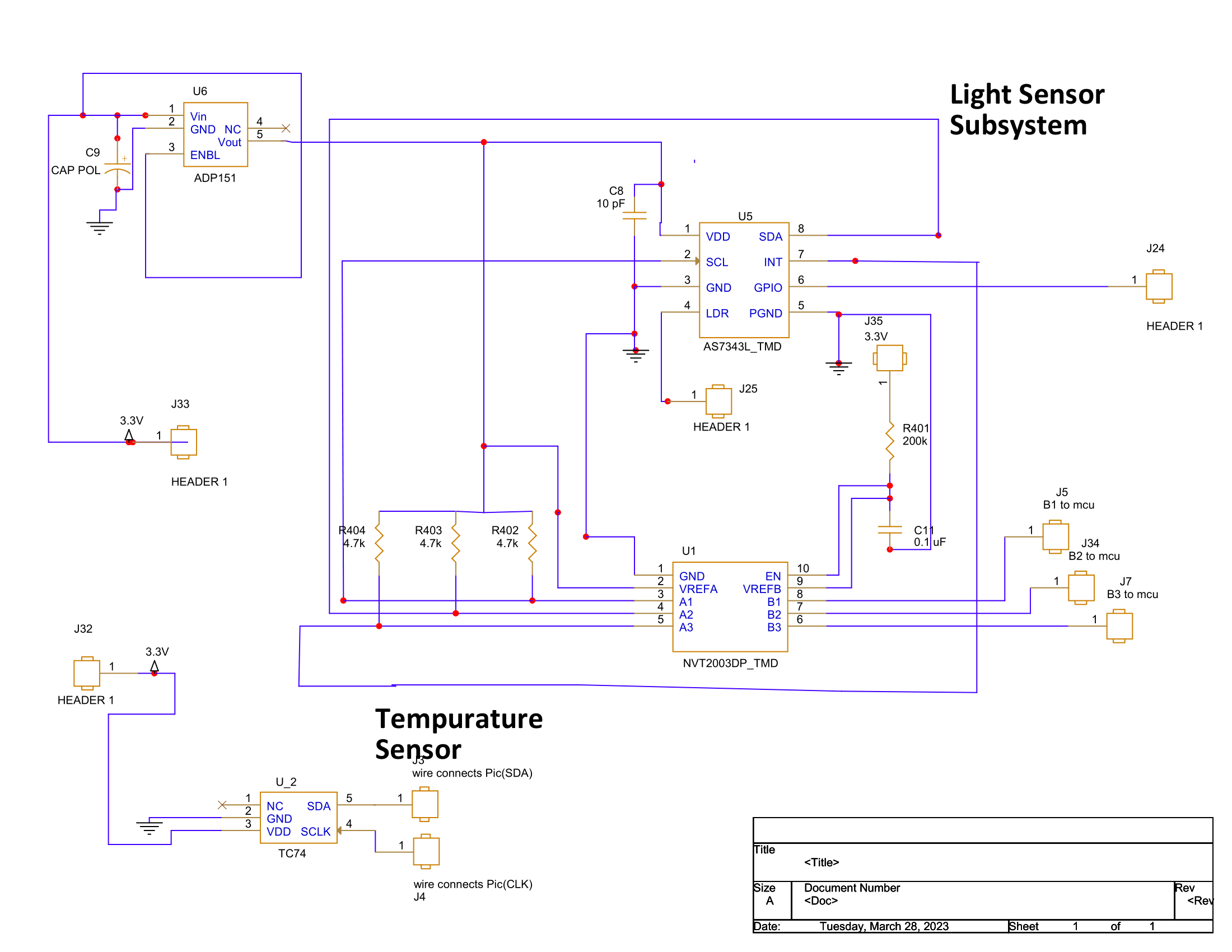
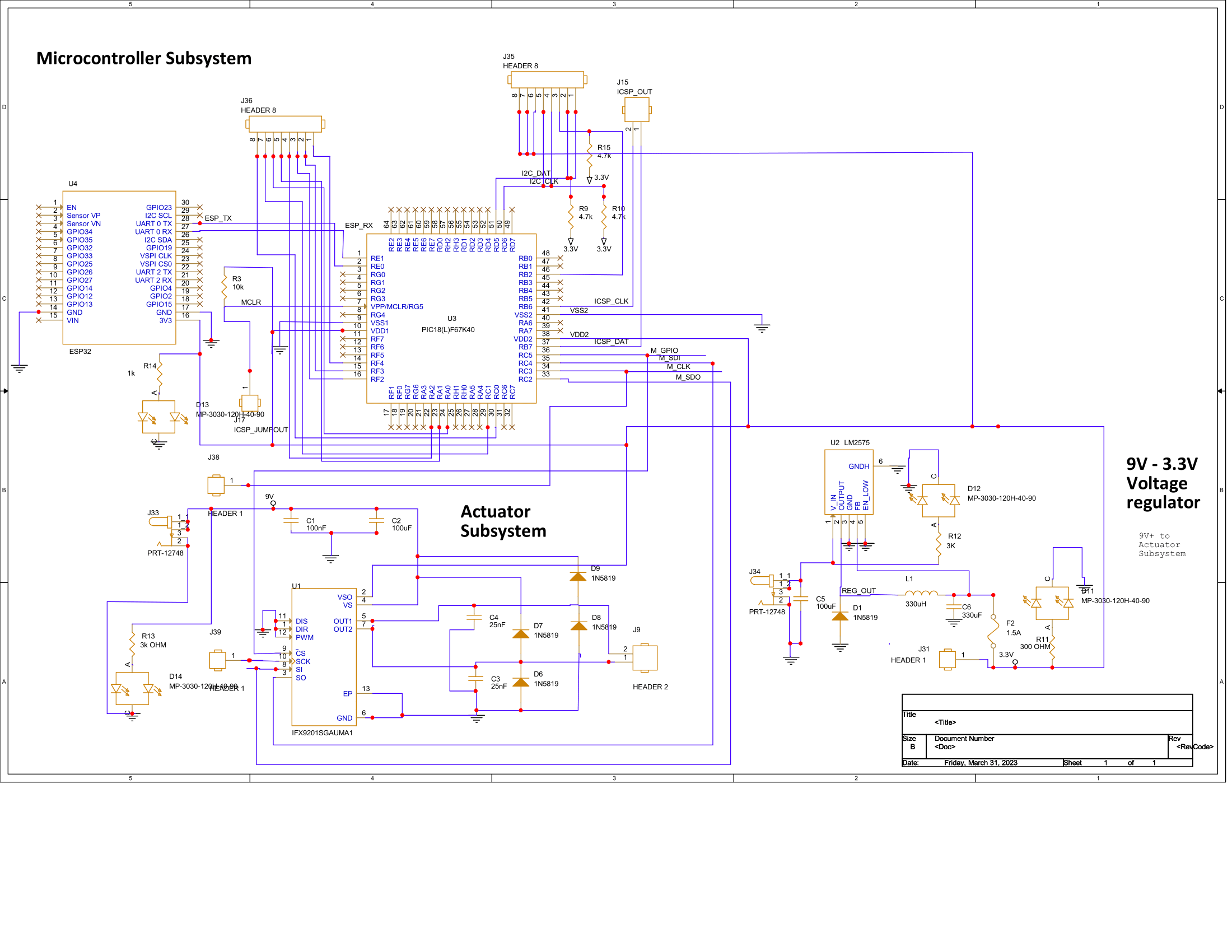
8.1 Team 305’s Final Schematic
8.2 Discussions (Functionality + Design and Descision Making)
For this project, a functional mobile weather station that can sense environmental conditions, manage motors, and wirelessly communicate data is presented in a schematic that aims to meet user needs and product requirements. There are four subsystems in the circuit design, each with unique components and functionalities.
An ambient light sensor that makes use of the I2C communication protocol is the first subsystem. For weather monitoring, the AS7343 L-DLGM light sensor is used to measure ambient light levels. The 1.8V output of the sensor is converted to 3.3V, the system’s logic level, using the voltage translator NVT2003. The voltage is controlled and a reliable power source for the sensor is provided by the low-dropout regulator ADP151. This subsystem complies with the product requirement of using at least two distinct serial sensors to sense at least two environmental conditions.
A temperature sensor, which is the second subsystem, also employs the I2C protocol for communication. Another crucial variable for weather monitoring is ambient temperature, which is sensed by the TC74A4-3.3VCTTR temperature sensor. Similar to the first subsystem, this subsystem satisfies the product’s needs and requirements.
A motor and motor controller that communicate using an SPI-based interface make up the third subsystem. The motor used by the 1568-ROB-15277-ND SparkFun Electronics is managed by the IFX9201SGAUMA1 motor controller. The product requirement that a subsystem have at least one motor controlled by a motor controller communicating via an SPI-based protocol is met by this subsystem.
A switching regulator and a microprocessor make up the fourth subsystem. All other subsystems are under the control of the microcontroller PIC18LF67K40, which also processes data. The voltage is controlled and a reliable power source for the entire system is provided by the LM2575S-3.3/NOPB switching regulator. This subsystem complies with the product specifications, which call for the use of the UART communication protocol and the inclusion of at least one switching voltage regulator in the finished project.
The schematic provided fits the user’s requirements for a practical, user-friendly, portable, durable device that generates correct data and requires little setup. Users’ safety is ensured by the low voltage and current requirements, and affordable production is made possible by surface-mount components. The device can be made smaller and more mobile to make it easier to use, and the Wi-Fi communication protocol enables direct access to the data the product is registering. The user’s desire for a satisfying experience is provided by the smooth connection to other devices, configurable parameters, and conveniently accessible database. Overall, the functionality of this design provides a dependable, effective, and configurable mobile weather station, satisfying both user needs and product requirements.
8.3 Final PCB Design
Top screenshot of final pcb main board
 Bottom screenshot of final main board
Bottom screenshot of final main board
 Top screenshot of final pcb sensor board
Top screenshot of final pcb sensor board
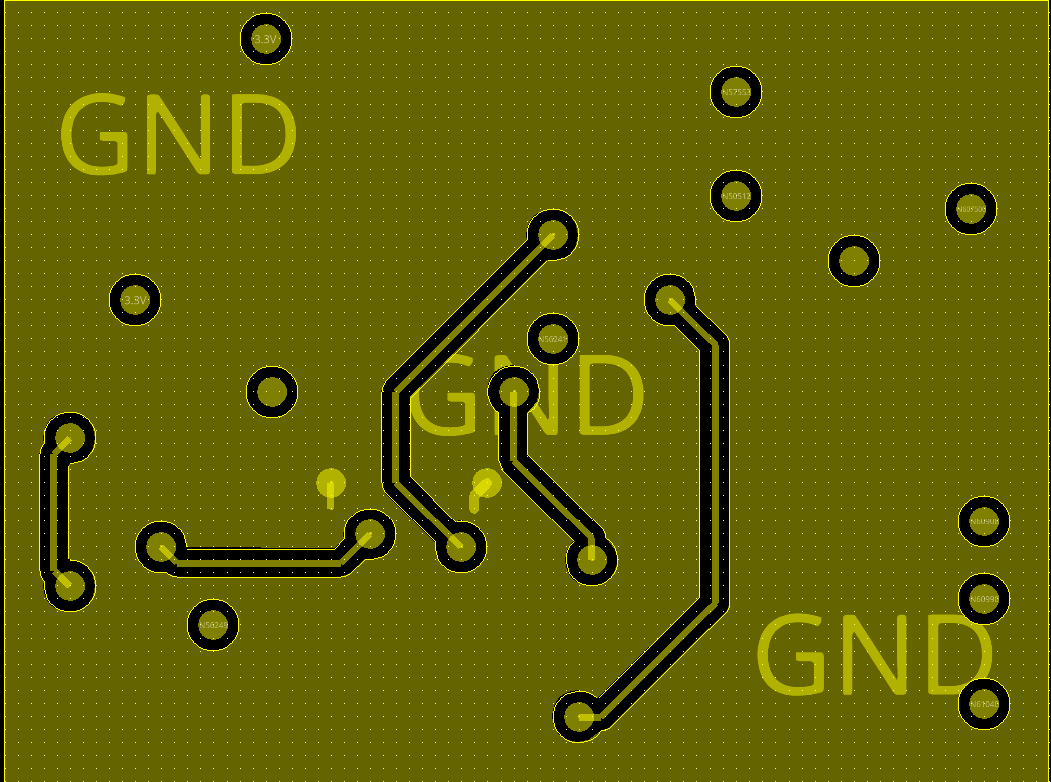
 Bottom screenshot of final pcb sensor board
Bottom screenshot of final pcb sensor board
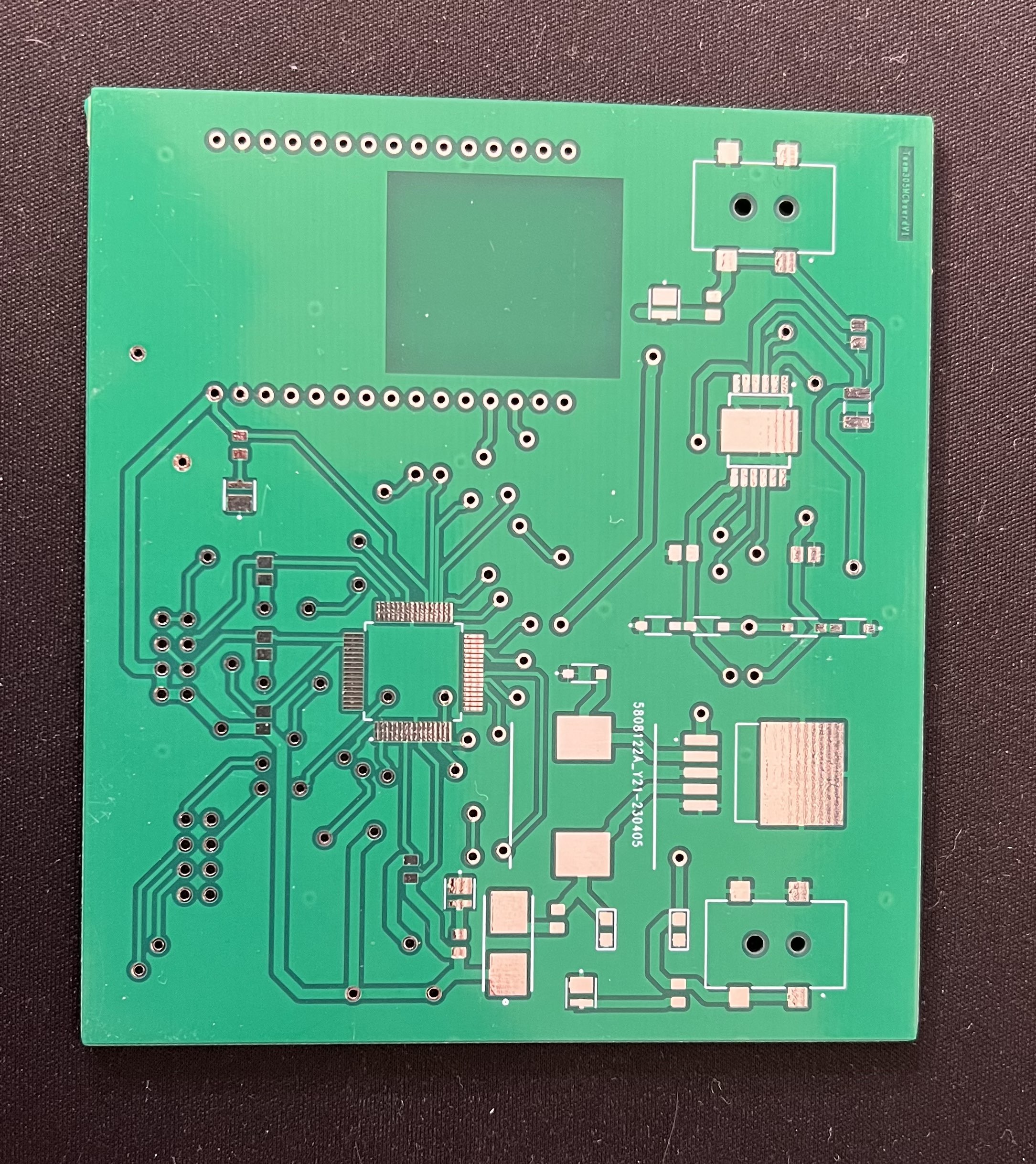
Top physical shot of final pcb main board
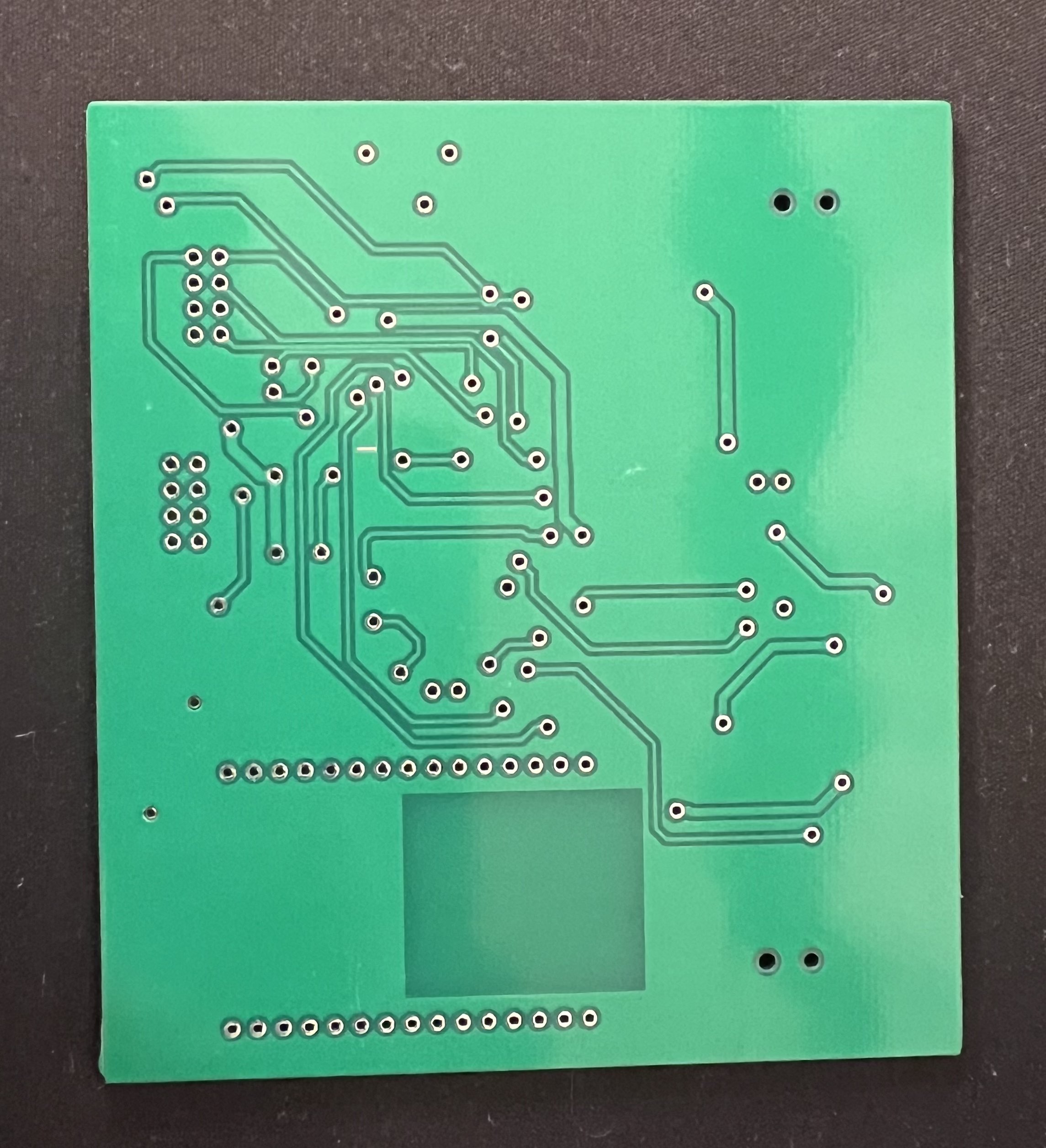
 Bottom physical shot of final main board
Bottom physical shot of final main board
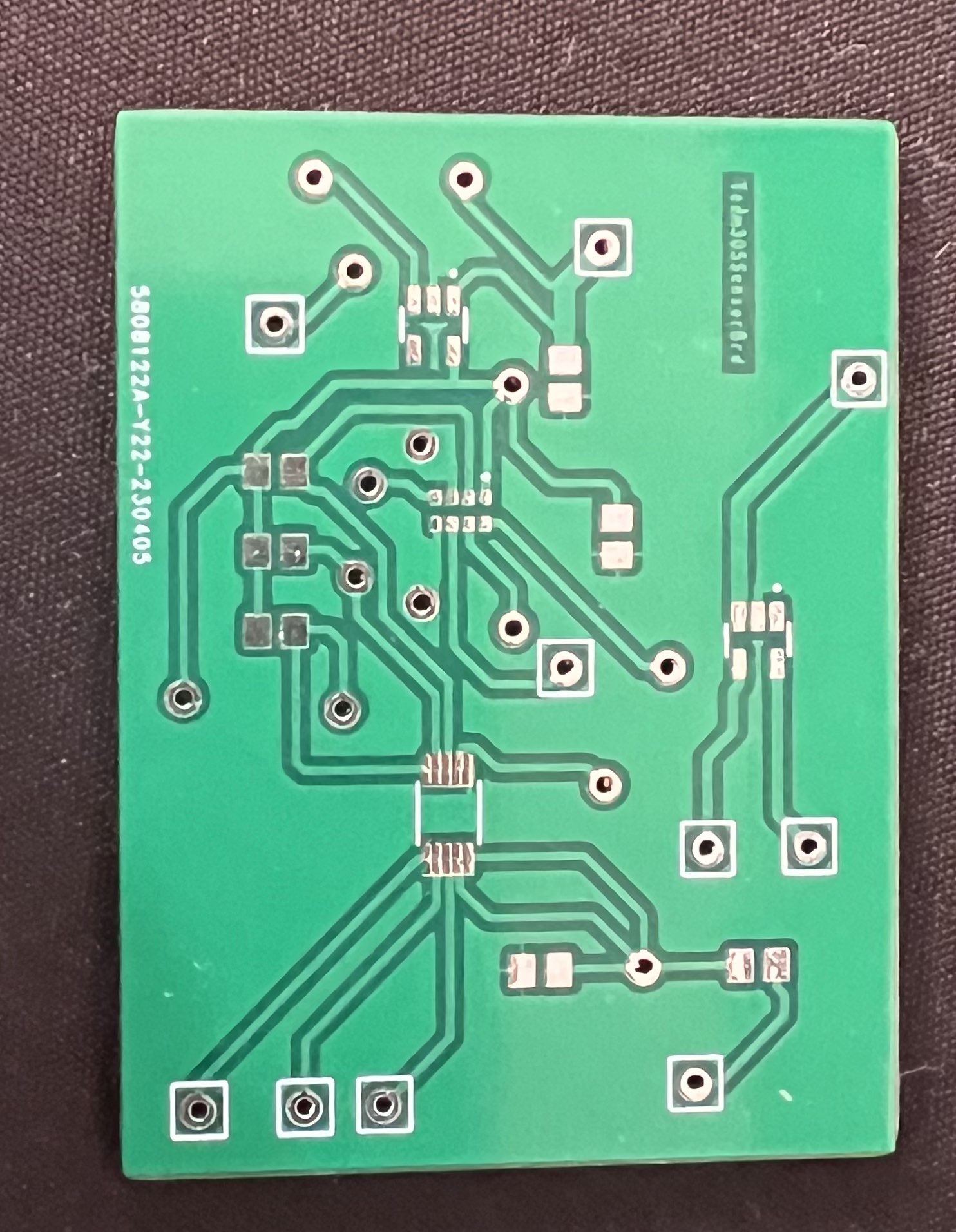
 Top physical shot of final pcb sensor board
Top physical shot of final pcb sensor board
 Bottom physical shot of final pcb sensor board
Bottom physical shot of final pcb sensor board
8.4 Version 2.0
If a version 2.0 were to be created, several changes to the hardware design would be implemented to enhance performance and usability.
The first modification involves the addition of a sensor that can gauge both humidity and temperature. The device’s ability to perform more efficiently as a mobile weather station would increase, resulting in data that is more accurate and trustworthy. Owners of greenhouses would particularly benefit from this function because maintaining the ideal temperature and humidity levels is essential for plant growth.
Second, the team wants to make the ambient light sensor better by using some code. This might be tough, but they think they can do it with more time and help from experts. If they succeed, the sensor will be able to measure all kinds of light. This would be helpful for users who want to know more about their environment.
Third, the team wants to update the motor driver. The motor driver can currently enable the SPI protocol, however there were numerous difficulties in doing so. The group would research upgrading to an SPI-based motor driver as a result. The device’s motors might be controlled more consistently with this adjustment.
For the last upgrade the team intends to replace the current 64-pin microcontroller with a PIC with around 24 pins, which would fulfill all necessary requirements. The current microcontroller’s 64 pins made it challenging to hand-solder and was not fully utilized, making it an unfavorable choice for the project.